Carbon Dioxide Contained in a Piston Cylinder Arrangement
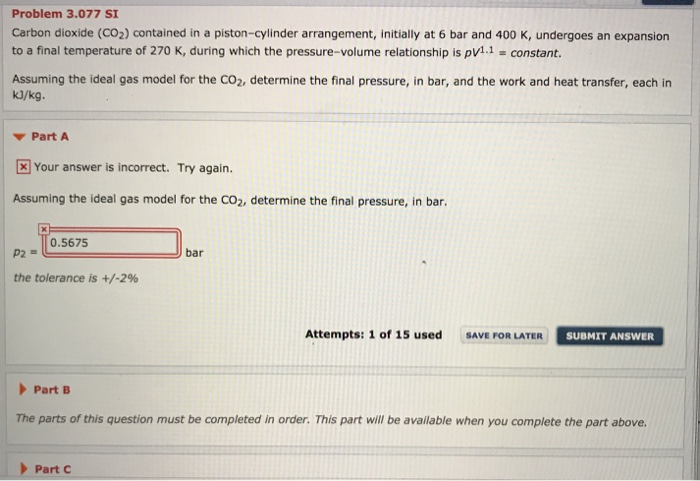
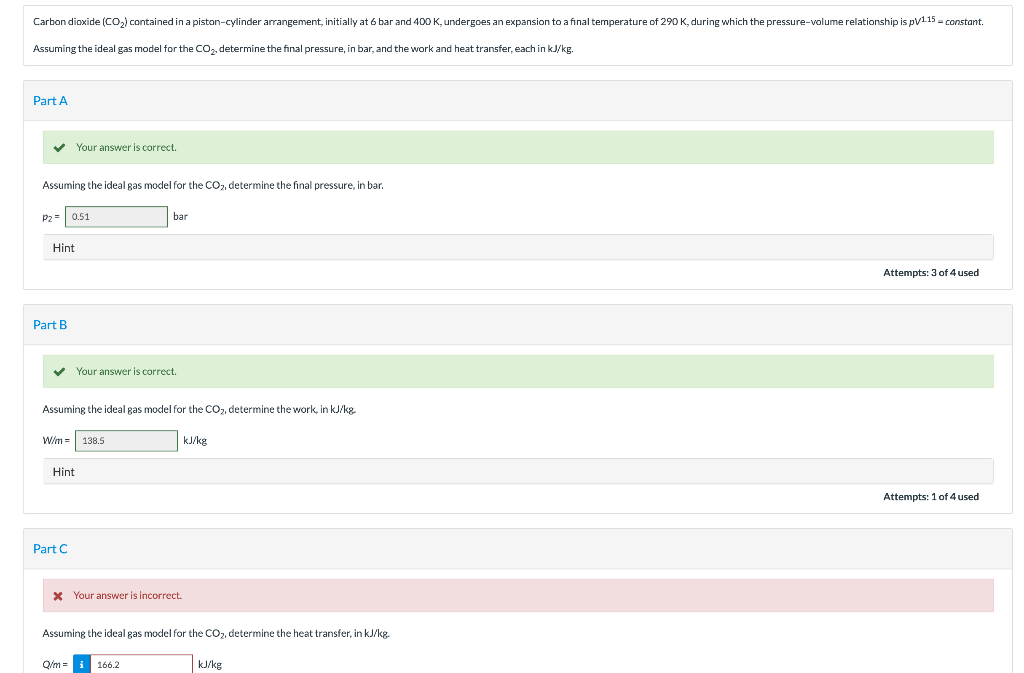
Carbon dioxide CO 2 contained in a pistoncylinder arrangement initially at 6 bar and 400 K undergoes an expansion to a final temperature of 250 K during which the pressurevolume relationship is pV 11 constant. The final pressure of the gas in the piston-cylinder.
Solved Problem 3 077 Si Carbon Dioxide Co2 Contained In A Chegg Com
Assuming the ideal gas model for the CO 2 determine𝑉 12 𝑐𝑎.

. P448 contains carbon dioxide at 50 mathrmlbf mathrmin2 200 mathrmF with a volume of 5 mathrmft3. Carbon dioxide CO2 contained in a piston-cylinder arrangement initially at 6 bar and 400 K undergoes an expansion to a final temperature of 298 K during which the pressure-volume relationship is pV12constant. Assuming the ideal gas model for the CO 2 determine the final pressure in bar and the work and heat transfer each in kJkg.
The metal piston has a density of 8000 kgm3 and the atmospheric pressure is 101 kPa. CO_ 2 C O2. Carbon dioxide contained in a piston-cylinder device is compressed from 03 to 01 m3.
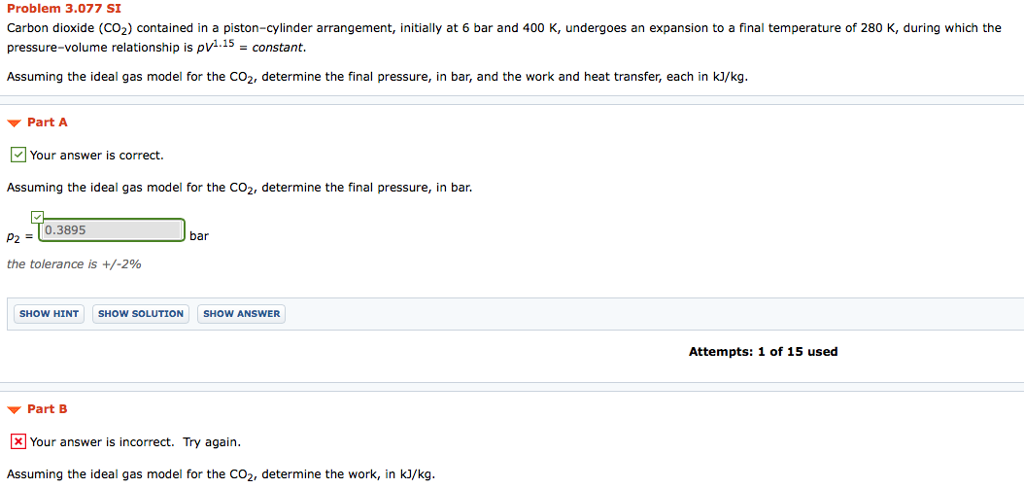
The total external force acting on the piston is proportional to V 3This system is allowed to cool to room temperature 20C. Assuming the ideal gas model for the CO2 determine the final pressure in bar and the work and heat transfer each in kJkg. Carbon dioxide CO2 contained in a pistoncylinder arrangement initially at 6 bar and 400 K undergoes an expansion to a final temperature of 280 K during which the pressurevolume relationship is pV11 constant.
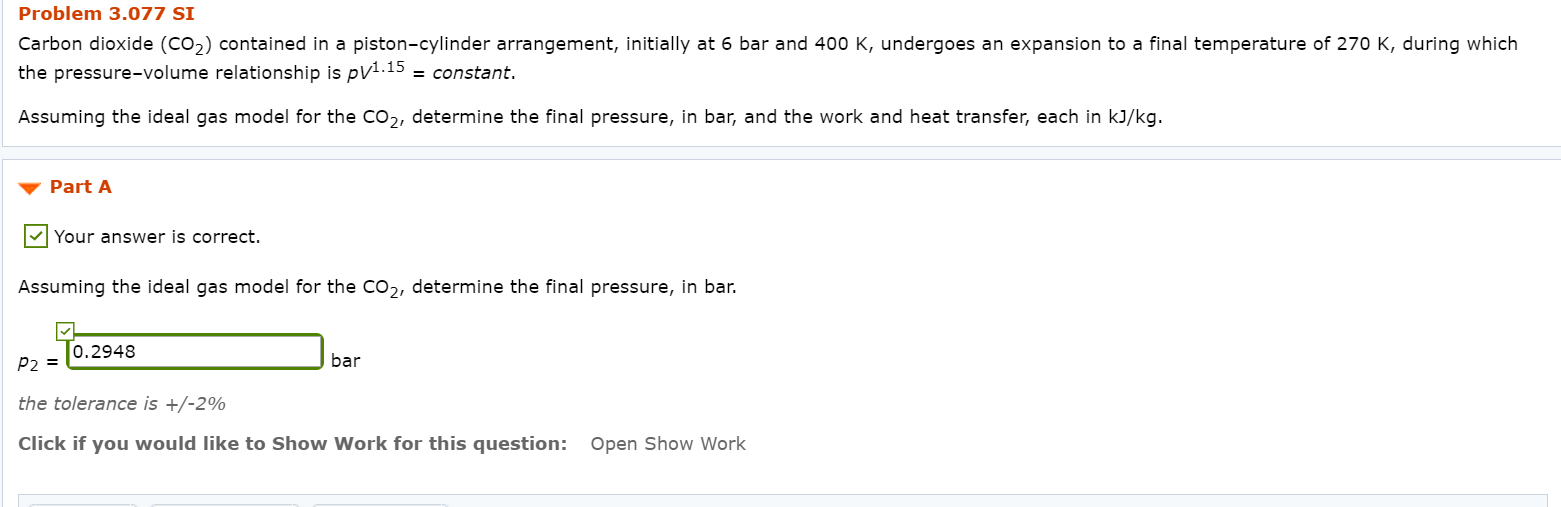
Carbon dioxide CO2 contained in a pistoncylinder arrangement initially at 6 bar and 400 K undergoes an expansion to a final temperature of 280 K during which the pressurevolume relationship is pV12 constant. Carbon dioxide CO2 contained in a pistoncylinder arrangement initially at 6 bar and 400 K undergoes an expansion to a final temperature of 298 K during which the pressure volume relationship is pV12 constant. Carbon dioxide CO 2 contained in a piston-cylinder arrangement initially at 6 bar and 400 K undergoes an expansion to a final temperature of 298 K during which the pressure-volume relationship is.
Carbon dioxide contained in a piston-cylinder device is compressed from 03 to 01 mathrmm3 During the process the pressure and volume are related by Pa V-2 where a8 mathrmkPa cdot mathrmm6. Assuming the ideal gas model for the CO2 determine heat transfer in kJkg. Contained in a pistoncylinder arrangement initially at 6 bar and 400 K undergoes an expansion to a final temperature of 298 K during which the pressurevolume relationship is.
During the process the pressure and volume are related by P aV-2 where a 8 kPam6. Carbon dioxide CO2 contained in a piston-cylinder arrangement initially at 6 bar and 400 K undergoes an expansion to a final temperature of 298 K during which the pressure-volume relationship is pV12 constant. Calculate the work done on the carbon dioxide during this process.
The pistoncylinder shown in Fig. Assuming the ideal gas model for the CO2 determine the final pressure in bar and the work and heat transfer each in kJkg. P V 12.
A piston-cylinder arrangement contains Carbon dioxide CO2 initially at 66 kPa and 400 K undergoes an expansion process with pressure-volume relationship of PV 12 Costantto a final temperature of 298 K. A cylinderpiston contains carbon dioxide at 1 MPa 300C with a volume of 200 L. Calculate the work done on the carbon dioxide during this process.
Assuming the ideal gas model for the CO2 determine the final pressure in bar and the work and heat transfer each in kJkg. Assuming the ideal gas model for the CO2 determine the final pressure in bar and the work and heat transfer each in kJkg. Work PdV P2 v2 P1 v1 1-n 1000 020596 3000 011619 1 1919 1552 kJ.
A pistoncylinder contains carbon dioxide at 300 kPa 100C with a volume of 02 m3. Assuming the gas to be an ideal gas determine the final pressure kPa the work done and the heat transfer each in kJ. Assuming the ideal gas model for the CO2 determine the heat transfer in kJkg.
Carbon dioxide contained in a piston-cylinder arrangement initially at 6 bar and 400K undergoes an expansion to a final temperature of 298 k during which the pressure-volume relationship if pV12 constant. Assuming the ideal gas model for the CO2 determine the final pressure in bar and the work and heat transfer each in kJkg. Determine the work done during the process.
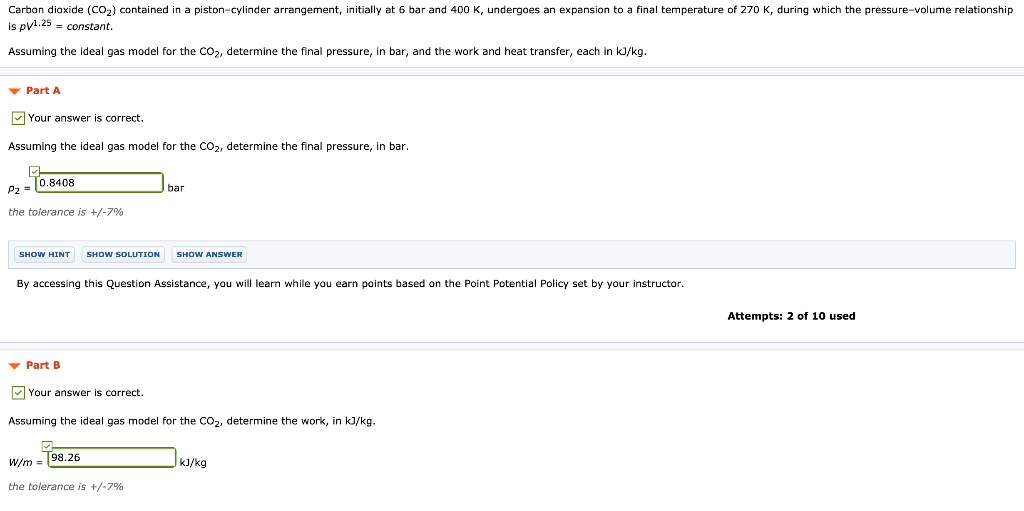
Carbon dioxide CO2 contained in a pistoncylinder arrangement initially at 6 bar and 400 K undergoes an expansion to a final temperature of 280 K during which the pressurevolume relationship is pV125 constant. The cylinder contains carbon dioxide at 200 kPa and ambient temperature of 290 K. Carbon dioxide CO2 contained in a pistoncylinder arrangement initially at 6 bar and 400 K undergoes an expansion to a final temperature of 298 K during which the pressurevolume relationship is pV12 constant.
Assuming the ideal gas model for the CO2 determine the final pressure in bar and the work and heat transfer each in kJkg. Solution for Carbon dioxide contained in a piston-cylinder arrangement initially at 6 bar and 400K undergoes an expansion to a final temperature of 298 k. Mass is added at such a rate that the gas compresses according to the relation P Y12 constant to a final temperature of 350 mathrmF.
Carbon dioxide CO2 contained in a pistoncylinder arrangement initially at 6 bar and 400 K undergoes an expansion to a final temperature of 300 K during which the pressurevolume relationship is pV125 constant.
Solved Problem 3 077 Si Carbon Dioxide Co2 Contained In A Chegg Com

Solved Carbon Dioxide Co2 Contained In A Piston Cylinder Chegg Com

Solved Carbon Dioxide Co2 Contained In A Piston Cylinder Chegg Com
Solved Carbon Dioxide Co2 Contained In A Piston Cylinder Chegg Com
Solved Problem 3 077 Si Carbon Dioxide Co02 Contained In A Chegg Com

Solved Carbon Dioxide Co2 Contained In A Piston Cylinder Chegg Com

Solved Carbon Dioxide Co2 Contained In A Piston Cylinder Arrangement Initially At 6 Bar And 400 K Undergoes An Expansion To Final Temperature Of 298 K During Which The Pressure Volume Relationship Is Pe Vl Constant

No comments for "Carbon Dioxide Contained in a Piston Cylinder Arrangement"
Post a Comment